User Interface#
The XRTwin user interface is designed to provide a comprehensive and intuitive workspace for creating and managing your virtual reality simulations. Let's explore the various components of the user interface.
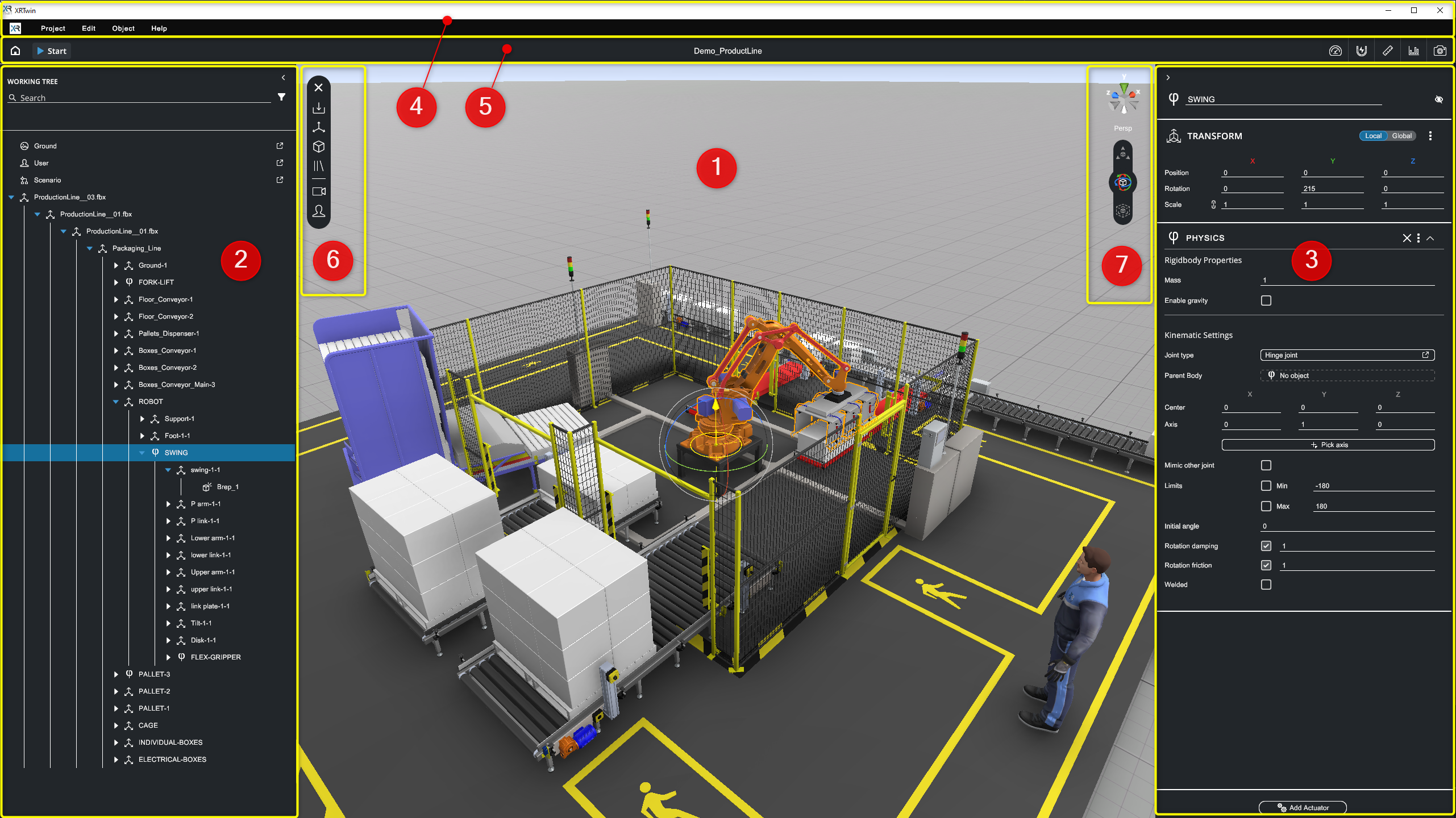
Editor mode VS Simulation mode
XRTwin offers two modes: Editor mode and Simulation mode.
- In Editor mode, users have complete freedom to modify the scene, add objects, and adjust properties.
- When starting Simulation mode (click Start button), scene modification is disabled, and objects behave according to physics laws.
- Stopping the simulation (click Stop button) resets object positions and returns to Editor mode, allowing for further editing and refinement. See Simulation.
1. Scene View#
The central area of the user interface is the Scene View, where all the 3D objects of your simulation are displayed. This is where you can interact with and visualize your virtual environment.
See Scene navigation presets and Object manipulation to learn more about actions you can do in the Scene View.
Shortcuts in Scene View
In Scene View, click to give it the focus. Then,
- Use the F key to center and focus on the selected object. Alternatively, double-click the object,
- Use the arrow keys to adjust the point of view. Use the Left, Right arrows to move it to the left or right (pan). Use the Up and Down arrows to move forward and backward by increments (zoom),
- Use mouse wheel to move forward and backward dynamically (zoom). Keep the cursor flying over the 3D view.
2. Hierarchy or Working Tree#
Located on the left panel, the Hierarchy panel (labeled Working Tree) provides a hierarchical list of all objects (nodes) in the scene, along with their relationships (parenting).
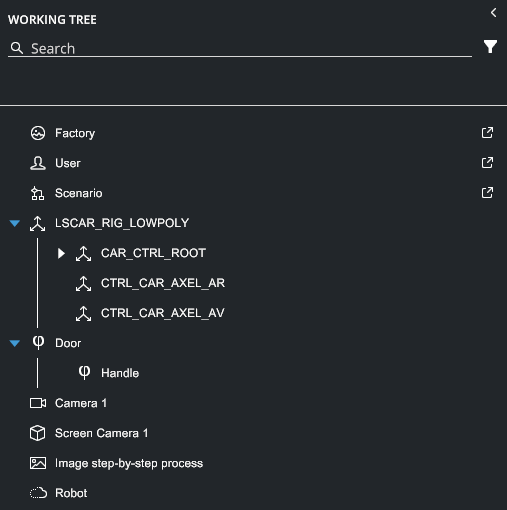
Each node type is represented by an icon, making it easy to identify different elements such as rigid bodies, models, and point clouds (see complete type list below).
Filters#
You can click on this button  and filter nodes by name or type for better organization and navigation.
and filter nodes by name or type for better organization and navigation.
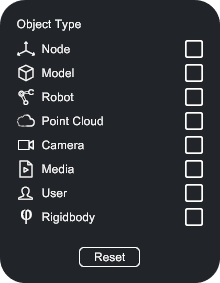
- Node: An empty node (without geometry)
- Model: A 3D model (a node with geometry)
- Robot: Coming soon
- Point Cloud: Imported point cloud (see Import Point clouds)
- Camera: Additional virtual cameras
- Media: Imported media (audio, video or image sources, see Imported Media files)
- User: The current User
- Rigidbody: Objects with physical properties (see Physics and interactions)
- Reset: Click to clear all filters.
Relationships#
The Hierarchy panel allows you to modify the relationships between objects by re-parenting them, by dragging a node and dropping it on an other.
Node context menu#
Use the node context menu to quickly perform the available actions.
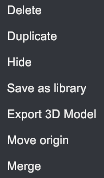
- Delete: Remove selected object from scene (shortcut Del). Not-undoable.
- Duplicate: Duplicate selected object. An offset is provided to make it easy to select and move.
- Hide / Show: Hide or show the current object. If an object is hidden, its physical behaviors are inactivated and ignored in the simulation (activated and taken in account, respectively).
- Save as library: Save the selected object and all of its children in the hierarchy graph (if applicable) to any directory of your choice, with the .xrlib extension.
It is recommended that you create a library folder accessible from all projects to store reusable objects, such as pallets, forklifts, screwdrivers, silhouettes for scale, workbenches, baskets, etc. You can then add these objects to any project later (from main menu, Object>Add>Add from library). - Export 3D Model: Export the selected object and all of its children in the hierarchy graph (if applicable) to any directory of your choice. Multiple CAD formats are available.
- Move origin: Edit selected part origin. XRTwin will provide remarkable propositions based on the object's topology (centers, perpendiculars, etc.). See Move part origin.
- Merge: A local process that combines all the child nodes of the selected parent into a single "Group" entity, reducing the number of draw calls and improving performance. This action can be reversed: right-click on the "Group" node and select "Unmerge" in the contextual menu. See Merge static objects
Shortcuts in Hierarchy panel
In Hierarchy panel, click to give it the focus. Then,
- Use the F key to center and focus on the selected object in the Scene View.
- Use the arrow keys Left, Right, Up, Down to move between hierarchical levels. Select the next or previous node on same level. Go up to the parent level or down to the child level. Levels expand and collapse automatically.
- Use mouse wheel to scroll the hierarchy list. Keep the cursor flying over the panel.
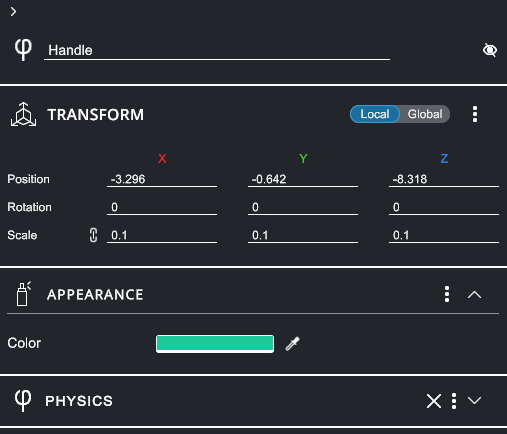
3. Property Panel#
The right panel of the user interface is the Property Panel. It provides contextual information about the selected objects such as their position, appearance, and physics properties.
The Property Panel allows you to enable/show or disable/hide the selected object  , change its name, and add or modify its attributes to fine-tune its behavior.
, change its name, and add or modify its attributes to fine-tune its behavior.
Expand sections to show all properties.
Copy Paste object properties#
In Editor mode, you can copy properties from selected object and paste them onto another.
Copy and paste in Property panel
Each component type uses a specific clipboard, so you can copy Transform, Physics and Appearance properties successively, for example. Then, you can select another object and corresponding component -- here Transform, Physics or Appearance -- and paste successively the properties.
To copy and paste multiple components in Edition mode:
- Select an object,
- In the source component, click the mini-menu
 button, then select Copy,
button, then select Copy, - If needed, do this for other relevant source components,
- Select another object,
- In the corresponding target component, click the mini-menu
 button again and select Paste. Values are replaced.
button again and select Paste. Values are replaced. - Repeat for each other relevant target component, if applicable.
Copy transforms values from Simulation mode to Edition mode
To copy transform values (Translation, Rotation, Scale) from Simulation mode to Edition mode, see Copy Transform workflow in What can I do in Simulation mode section.
4. Header and Menu Bar#
The Windows header bar allows you to display XRTwin in full screen mode, minimize or resize its window.

Located to the left of the Menu Bar, you will find the main menu with Project, Edit, Object, and Help drop-down menus.
Project menu#
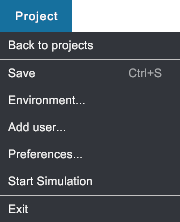
- Back to projects: Returns to the Launcher. Same as Home button
 .
. - Save: Save your project. Shortcut S.
- Environment...: Select a background for your scene.
- Add user...: Guided user selection based on the hardware you want to use.
- Preferences...: Select user settings at project level.
- Start Simulation: Launch the simulation session. Same as Start button
 .
.
Edit menu#
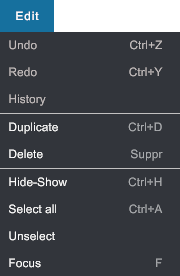
- Undo: Coming soon. Currently only transforms can be undone.
- Redo: Coming soon.
- History: Coming soon.
- Duplicate: Duplicate selected object. An offset is provided to make it easy to select and move. Shortcut Ctrl+D.
- Delete: Remove selected object from scene (shortcut Del). Not-undoable.
- Hide / Show: Hide or show the current object. If an object is hidden, its physical behaviors are inactivated and ignored in the simulation (activated and taken in account, respectively).
- Select all: Select all the nodes. Shortcut Ctrl+H.
- Unselect: Clear selection. Shortcut Esc.
- Focus: focus the camera on selected object, sets the zoom sensibility and changes the orbit rotation center.
Object menu#
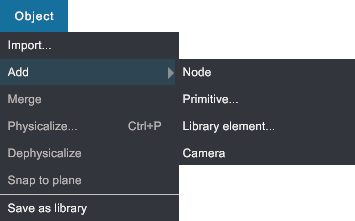
- Import...: Import your files in your scenes. Multiple formats are available for CAD and Mesh files (see Import CAD files, Point clouds (see Import point clouds) or media files (images, audio files and video movies, see Import media files.
- Add Node: Add an empty node as child as the current node (or root node).
- Add Primitive...: Add primitives in the scene (cube, sphere, capsule...).
- Add Library element: Add all objects saved in a
*.xrlibfile in the scene. You can replace selected node or add them at root level. - Add Camera: Add a virtual camera and its virtual screen in the scene. The video stream from this camera is displayed on the virtual screen. You can also choose to display it on one of the additional real screens managed by your computer.
- Merge: See context menu.
- Physicalize...: Guide you to select the physical behavior you want to apply on selected object(s). Shortcut P.
- Dephysicalize: The PHYSICS component is removed from selected object(s). All physical behaviors are deleted. Cannot be undone.
- Snap to plane: Coming soon.
- Save as Library: See context menu.
Help menu#
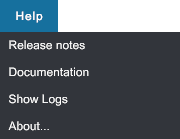
- Release notes: Open the release notes page in your web browser. See Release notes.
- Documentation: Open XRTwin online documentation in your web browser. See XR Twin Documentation.
- Show Logs: Open C:\Users\username\AppData\LocalLow\LSGROUP\XRTwin folder where you can find the application log files Player.log (current (last) session log file) and Player-prev.log (previous session log file). Sending both files along with your description to support can help our team identify the issues you are experiencing.
- About...: Open the "About" window where you will find version number, documentation and release notes links, copyright and more.
5. Tool Bar#
The top section of the user interface features the Tool Bar, which contains several essential options.

 to go back Home, to the Project Launcher screen.
to go back Home, to the Project Launcher screen.
 to start and stop the simulation.
to start and stop the simulation.- In the center is the project name (here Demo_ProductLine).
 At the right side, you will find various tools such as (from left to right) Optimize tool, Snapping tool, Measuring tool, Statistics panel and Make Screenshots, enhancing your control and analysis capabilities.
At the right side, you will find various tools such as (from left to right) Optimize tool, Snapping tool, Measuring tool, Statistics panel and Make Screenshots, enhancing your control and analysis capabilities.- Optimize scene tool: Merge static objects. See Merge static objects section for how to and restrictions.
- Snap object tool: Stick selected object to another. First, click to select the face of the source object to be snapped. Then, fly over the target face (must be on another object. If needed, use the shortcut I to invert snapping direction. Click to validate.
- Measure tool: Measure distances. Click on the first point, then the second. Short distance is indicated in millimeters. To decompose measures on XYZ axes, from main menu go to Project>Preferences>Graphics and check Show measure XYZ decompo. Fly over and click on the trash can to delete. The measurements persist between Editor and Simulation modes, but are not saved with your project. For measures in VR, see the Measure tool in the VR Menu.
- Show Statistics panel: Display the Statistics panel. In Editor mode, the panel displays the graphics performance (frame rate) and the number of objects, polygons and rigid bodies in the scene.
In Simulation mode, it displays the physics update duration / default allowed time (hold it below allowed time for maximum physical frame rate). In milliseconds (ms). - Take Screenshots tool: Use the Take Screenshot tool to capture images. See Take screenshots for tips and quick images folder access.
Easily find your screenshots#
Screenshots are saved in the Screenshots subfolder within your projectID directory. To easily open this folder, follow one of this tips.
-
Immediately after taking a screenshot, a capsule appears at the bottom of your Scene view. Click the “Review” link to immediately open the Screenshots folder in Explorer.
-
To open the folder later, return to the Launcher and press Alt+Shift+F9. Select your project card, open its mini-menu
 and click Open in explorer.
and click Open in explorer.
Windows Explorer will open with your current projectID directory selected. The name is such as7fa987a3-5356-41be-af6a-f9a502b78b6f. Open this folder, then open the Screenshots subfolder. All your screenshots are here (if you took any).
Do not inadvertently change ProjectThumbnail.png.
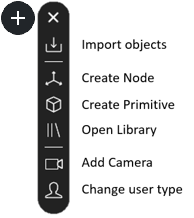
6. Quick Access Bar#
Located above the Scene View on the left, the Quick Access Bar offers quick and convenient access to frequently used operations. This bar includes options to import objects and elements from the library, change the user type (Desktop or VR), and create primitive objects for quick prototyping and scene setup.
Click the Quick Access button  to expand.
to expand.
7.1 View Gizmo#
Located at the top right of the scene view, the View Gizmo tool provides essential functionality for adjusting the camera view switching between predefined camera views such as top, side, and left providing a convenient way to view the scene from different perspectives or orthogonal projections.
7.2 Manipulation bar#
Located below the View Gizmo, this toolbar provides essential functionality for manipulating objects. Click on the icons to switch between translation, rotation, and scale modes and manipulate selected object gizmo with your mouse.
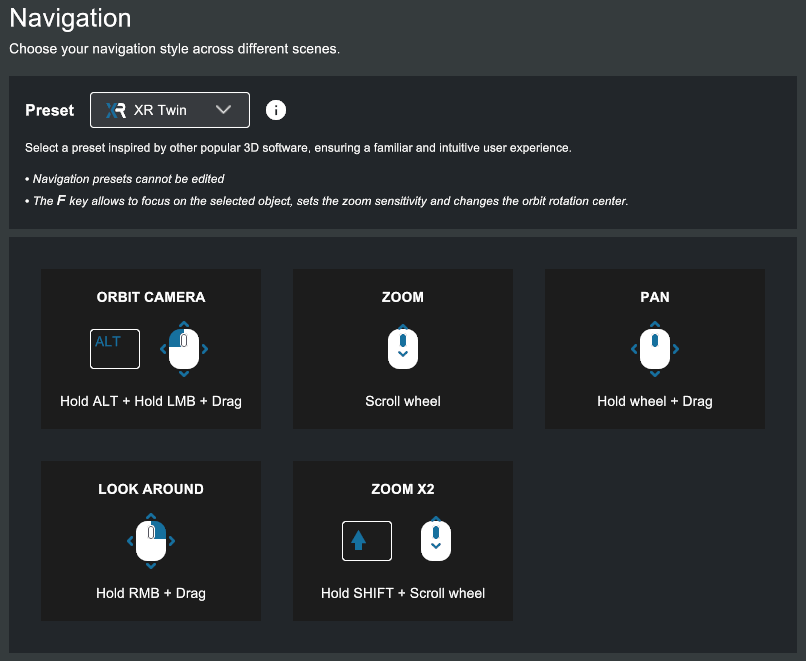
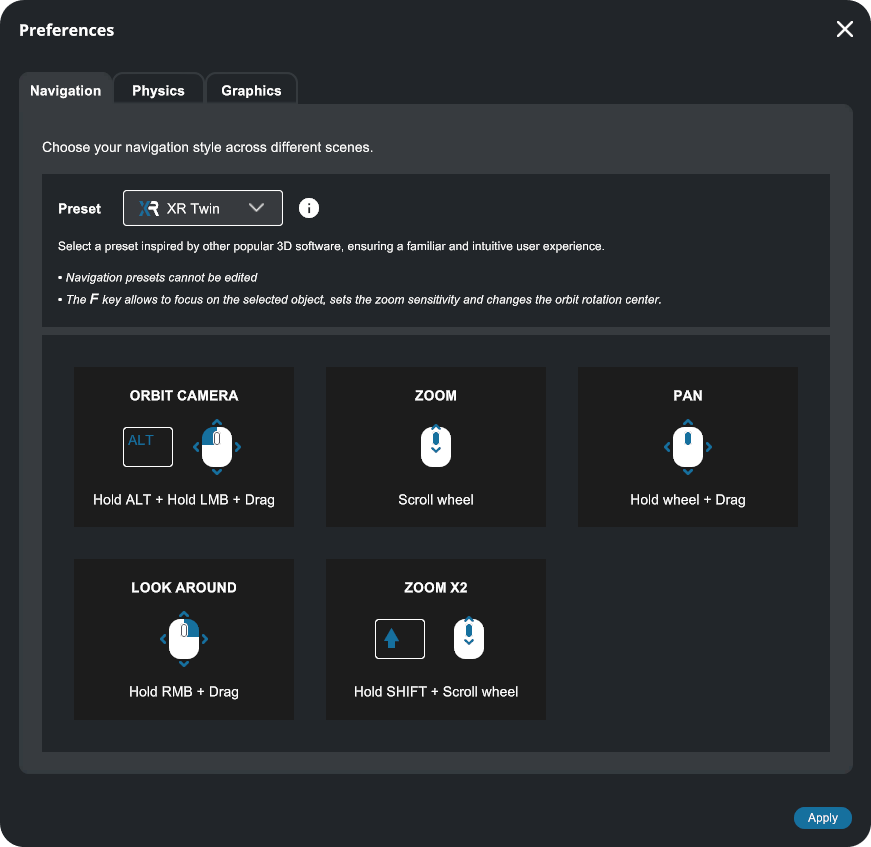
Scene navigation presets#
Several navigation style Presets are available in XR Twin. The keyboard and mouse shortcuts you use to move the viewpoint depend on the selected preset. Current Preset Default is XR Twin style (see shortcuts in image below).
For beginners
We recommend starting with XR Twin’s default navigation style preset for the best experience.
Select your navigation style preset#
If you’re accustomed to CAD design software, you might prefer to adjust your navigation preferences. XRTwin offers preset navigation styles tailored to popular CAD tools.

You can set your preferred navigation preset globally, at the application level, ensuring all new projects default to your chosen style, or you can set it at project level.
To select your global favorite navigation preset from the Project Launcher:
- From the left panel, select Settings to display the Settings panel.
- In the Navigation section, pull down the Preset dropdown list.
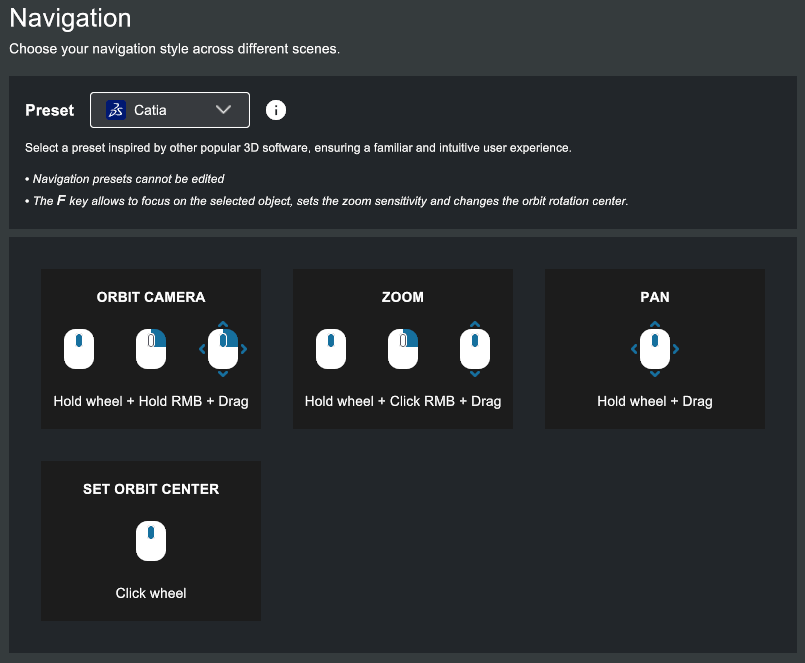
- Select the software whose navigation shortcuts you want to use: Sketchup, Catia, Solidworks, Inventor or Revit, or stick with the default XR Twin preset.
- Each preset displays its associated shortcuts (see XR Twin and Catia presets below).
- Your choice will apply to all new projects.
To select per project your favorite navigation preset from an opened project:
- With your project opened in EDITION Mode,
- From the main menu, go to Project>Preferences... to open the Preferences window.
- Select the Navigation tab.
- Next to Preset, expand the drop-down menu and select your favorite navigation preset (same as above).
- Click Apply to save and close the window.
- Your choice will only apply to the current project.
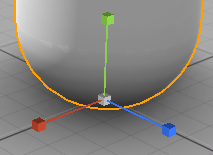
Object manipulation#
Located at the node reference point in the scene (pivot point), the move gizmos switch between translation, rotation and scale modes for the selected object, depending Manipulation Bar current option. The axes' direction depends on the current option of Local/Global and the hierarchy's parent transforms.
Translation gizmo#
The translation gizmo represents the three local or global XYZ translation axes, as well as the three corresponding planes.
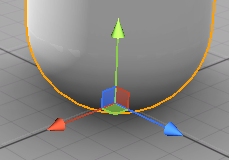

- Drag one of the three colored arrows (RGB) with the mouse to move the node in the desired direction (the X, Y, and Z axes, respectively).
- At the base of the gizmo, you will find colored squares (RGB). Click with the mouse to drag the node onto the corresponding plane (XZ, ZY, XY, respectively).
Rotation gizmo#
The rotation gizmo represents the three possible rotations around the local or global XYZ axes.
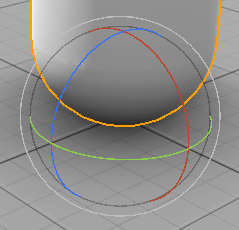

- Rotate one of the colored wheels (RGB) with the mouse to rotate the node around the desired axis (XYZ, respectively).
Scale gizmo#
The scale gizmo represents the three possible scaling options, according to the local or global XYZ axes.

- Drag one of the colored cubes (RGB) with the mouse to stretch the node on the selected axis (XYZ, respectively).
- At the base of the gizmo you will find a white cube. Click on it with the mouse and drag to perform a uniform scale change on all three axes simultaneously.
Local mode / Global mode#
If the node's TRANSFORM is in Local mode, then the gizmo orients itself according to the object's local coordinate system, which takes into account the orientation of its parents.
However, if the node's TRANSFORM is in Global mode, then the gizmo orients itself according to the scene's global coordinate system, regardless of the orientation of its parents.

Incremental moves#
Holding down the Shift key when you move a gizmo, you can perform incremental moves:
- Incremental translations (default steps of 0.5 m).
- Incremental rotations (default steps of 10°).
- Incremental scalings (default steps of x0.5).
The XRTwin user interface is thoughtfully designed to minimize the time required to create incredible and realistic simulations. Experience the efficiency and speed of XRTwin as you bring your virtual reality visions to life in a fraction of the time it would traditionally take.